
Unit Plan: Plate Tectonics
Science / Grade 8

Big Ideas
The Theory of Plate Tectonics is the unifying theory that explains Earth’s geological processes.
Concepts:
- Convection
- Density
- Forces
- Theories
Essential Questions
Students will keep considering…
- How do plate interactions help to determine risk to humans and the environment?
- What causes the surface of the Earth to change?
- How does what we see today unveil the Earth’s past?
- How can we predict and understand changes to the surface of the Earth?
Evaluative Criteria
- An accurate explanation of how earthquakes develop
- An accurate understanding of the processes under the Earth’s crust
- Interpreting information from data to support their arguments
- The use of multiple representations (diagrams, tables, graphs, etc…) to support their understanding of the topic
- The use of The Theory of Plate Tectonics to determine our risk level for earthquakes in the Lower Mainland
- A clear and understandable explanation, suited to the audience
Adaptation: Have students label a diagram of the earth
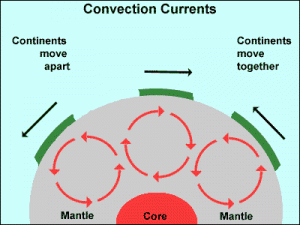
Extension: Students can create an analogy to the syrup and cracker
Adaptation: Have students label a convection diagram
Looking for accuracy of explanation and if they used multiple representations to help explain
Accuracy
Reflection, thoughtfulness and accuracy of journal entries
Qualitative and Quantitative observations
Monitoring Progress
Pre-assessment: Use the class brainstorm to see what the students know about the topic already and what questions need to be answered.
Do a class wonderwall – have students put up questions they have about the earth so that you can address the questions throughout the unit.
Some sample True/False Questions
True/False
1. Continents are smaller now than they were in the past.
2. The size of the earth is gradually increasing over time because of seafloor spreading.
3. Tectonic plates float on melted magma that is just below the surface of the earth.
4. The Earth’s mantle is made up of molten rock.
5. The edge of a continent is a plate boundary.
6. The amount that a tectonic plate moves during a person’s life is measurable.
7. Earthquakes are rare events.
8. Scientists cannot predict earthquakes.
9. Vancouver will not fall off into the ocean.
10. Earthquakes occur only on the Ring of Fire.
11. Volcanoes can form when a plate moves over a hot spot.
12. Magma comes from Earth’s outer core.
13. An inactive volcano may erupt again some day.
14. Volcanic eruptions occur randomly.
15. All mountains can become volcanically active.
16. Rocks give us clues about the Earth’s history.
Density:
Students may not have experienced the concept of density formally at this point. This is an opportunity to do a density lab where you can graph the data and explain the difference between qualitative and quantitative data. As well as students using mathematical formulas
See link to density lab in Resources
Potential Students Misunderstandings:
- Plates are metres thick
- Plates are melted rock
- Earth’s plates are separated by empty gaps
- Rocks are always solid
- The layer beneath Earth’s plates mostly consist of liquid rock material
- The layer beneath Earth’s plates mostly consist of solid rock material
- Continents only move inches over hundreds of years, not feet or miles
- Continents and ocean basins move, but so slowly that they will barely have moved after hundreds of years
- Earth’s plates move by floating on a layer of melted rock
- Earth’s plates cannot bend
- Mountains form by the piling up of pieces of rock
- Continental plate material is only pushed upward when it pushes into continental plate material on another plate
- When two plates move away from each other, loose rock material fills the empty gap that forms between them
Resources
Books
- BC Science 10
- What If? By Randall Munroe
- Science Formative Assessment by Page Keeley
- Making Thinking Visible by Ron Richhart
Websites
Reflection
How will teachers and their students reflect on and evaluate the completed project?
Teacher:
Next time I teach this unit I would…
Allow students to select the short stories that link to Identity.
Student:
My students needed:
Process:
Product:
Content:
Potential Student Misunderstanding:
Downloads
Stage 2 – Evidence
Authentic Performance Tasks
AUTHENTIC PERFORMANCE TASK: Assessing for Understanding
Students will be able to demonstrate their understanding by:
GRASPS
What is a GRASPS task?
Other Evidence
OTHER EVIDENCE: Assessing for Knowledge and Skills
Students will show they have acquired Stage 1 knowledge and skills by:
FORMATIVE
Layers of the Earth
- Analogy to chocolate bar
> Adaptation – students can just match the layers with layers of earth, no explanation needed or they can label a diagram that you provide for them
> Extension – have students come up with their own analogy (NOT the chocolate bar)
Convection
- Using the words mantle, crust, heat, less dense, movement, describe convection currents in the Earth
Tectonic Plate movements
- Odd One Out – use similar items and challenge students to choose which item in the group does not belong. Students are to justify their reason for selecting the item that does not fit with the others.
Theory of Plate Tectonics
- On Solid Ground – article on Wegner’s development of his theory
> Thinking Routines – Connect-Extend-Challenge. (page 132 in Making Thinking Visible)
> Class brainstorm of the evidence for the movement of the plates from the article
Plate Tectonics and Earth’s features
- Have student pick a certain geological feature or an Earth event (student choice) and explain how these are formed through their understanding of plate tectonics
> Examples: volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, mountain ranges (BC coastal mountains, The Rockies, The Alps, etc..), Tsunamis, Geysers, etc…
Geological formations and Changes to Earth
- Chalk talk (page 78 in Making Thinking Visible)
- Circle of Viewpoints – perspective taking (page 171 in Making Thinking Visible)
- Sentence – phrase – word (page 207 in Making Thinking Visible)
Quizzes
- Quizzes can be used to check-in after acquisition lessons
Science Journals
- Use the science journals to see how they students are thinking but also to see what questions the students have
Lab Activities
- Use lab activities to asses students skill at making qualitative and quantitative observations
- Density lab – great opportunity to incorporate graphing skills and mathematical computations using formulas

The following resources are made available through the British Columbia Ministry of Education. For more information, please visit BC’s New Curriculum.
Big Ideas
The Big Ideas consist of generalizations and principles and the key concepts important in an area of learning. The Big Ideas represent what students will understand at the completion of the curriculum for their grade. They are intended to endure beyond a single grade and contribute to future understanding.
Core Competencies
 Communications Competency
Communications Competency
The set of abilities that students use to impart and exchange information, experiences and ideas, to explore the world around them, and to understand and effectively engage in the use of digital media
 Thinking Competency
Thinking Competency
The knowledge, skills and processes we associate with intellectual development
 Social Competency
Social Competency
The set of abilities that relate to students’ identity in the world, both as individuals and as members of their community and society
Curricular Competencies & Content
Curricular Competencies are the skills, strategies, and processes that students develop over time. They reflect the “Do” in the Know-Do-Understand model of curriculum. The Curricular Competencies are built on the thinking, communicating, and personal and social competencies relevant to disciplines that make up an area of learning.
Additional Resources
First People's Principles of Learning
To read more about First People’s Principles of Learning, please click here.
For classroom resources, please visit the First Nations Education Steering Committee.
